The problem is not too much money printing, the problem is too little debasement because inflation remains very low.
So argued Nouriel Roubini, a left leaning economist who effectively in one sentence has somewhat summarized a new Modern Monetary Theory (MMT) that is gaining traction among the Davos men.
“The experience with the money printing of the central banks in the past decade has led to a rethinking for many observers. Although central banks have pumped trillions of dollars into the markets and have created new debt for states, companies and households, inflation is slowing down and interest rates are still at extremely low levels.
Not a few experts demand a general inventory of economic theories of money in the face of paradoxical conditions. The printing of money by the central banks and debt of the states is no longer a danger in this brave new world, but rather a promise. The new formula that combines both is MMT. That stands for Modern Monetary Theory.”
So says one of the Davos men according to a rough translation. This new theory is somewhat old and goes back to Georg Friedrich Knapp, the man accused of giving intellectual cover to the detachment of money from gold as a base.
These new economists, who cite as intellectual inheritance such distinguished men like Karl Marx and John Maynard Keynes, argue that:
“The balance sheet of the government does not include any domestic monetary instrument on its asset side; it owns no money. All monetary instruments issued by the government are on its liability side and are created and destroyed with spending and taxing/bond offerings, respectively.”
That is, the government creates money and according to John T. Harvey, the word borrowing is a misnomer when it comes to a sovereign government’s fiscal operations, because what the government is doing is accepting back its own IoUs, and nobody can borrow back their own debt instruments.
They are saying that the current view which states the Fed controls inflation and unemployment by setting interest rates is incorrect because the effect the Fed would have would depend on the demand for money/loans.
Such demand can come from the government which can create as much money as it pleases and can use taxation or debt issuance to destroy the money created and thus to lower supply if inflation increases. According to a summary:
“A sovereign government typically has an operating account with the country’s central bank. From this account, the government can spend and also receive taxes and other inflows. Each commercial bank also has an account with the central bank, by means of which it manages its reserves (that is, the amount of available short-term money that it holds).
When the government spends money, the treasury debits its operating account at the central bank, and deposits this money into private bank accounts (and hence into the commercial banking system). This money adds to the total deposits in the commercial bank sector. Taxation works exactly in reverse; private bank accounts are debited, and hence deposits in the commercial banking sector fall.
Virtually all central banks set an interest rate target, and conduct open market operations to ensure base interest rates remain at that target level. According to MMT, the issuing of government bonds is best understood as an operation to offset government spending rather than a requirement to finance it.
In most countries, commercial banks’ reserve accounts with the central bank must have a positive balance at the end of every day; in some countries, the amount is specifically set as a proportion of the liabilities a bank has (i.e. its customer deposits). This is known as a reserve requirement.
At the end of every day, a commercial bank will have to examine the status of their reserve accounts. Those that are in deficit have the option of borrowing the required funds from the central bank, where they may be charged a lending rate (sometimes known as a discount rate) on the amount they borrow.
On the other hand, the banks that have excess reserves can simply leave them with the central bank and earn a support [savings] rate from the central bank. Some countries, such as Japan, have a support rate of zero.
Banks with more reserves than they need will be willing to lend to banks with a reserve shortage on the interbank lending market. The surplus banks will want to earn a higher rate than the savings rate that the central bank pays on reserves; whereas the deficit banks will want to pay a lower interest rate than the interest rate the central bank charges for borrowing.
Thus they will lend to each other until each bank has reached their reserve requirement. In a balanced system, where there are just enough total reserves for all the banks to meet requirements, the short-term interbank lending rate will be in between the savings rate and the interest rate.
Under an MMT framework where government spending injects new reserves into the commercial banking system, and taxes withdraw it from the banking system, government activity would have an instant effect on interbank lending.
If on a particular day, the government spends more than it taxes, reserves have been added to the banking system. This will typically lead to a system-wide surplus of reserves, with competition between banks seeking to lend their excess reserves forcing the short-term interest rate down to the savings rate (or alternately, to zero if a savings rate is not in place). At this point banks will simply keep their reserve surplus with their central bank and earn the savings rate.
The alternate case is where the government receives more taxes on a particular day than it spends. In this case, there may be a system-wide deficit of reserves. As a result, surplus funds will be in demand on the interbank market, and thus the short-term interest rate will rise towards the Fed’s interest rate level.
Thus, if the central bank wants to maintain a target interest rate somewhere between the savings rate and the interest rate, it must manage the liquidity in the system to ensure that there is the correct amount of reserves in the banking system.
Central banks manage this by buying and selling government bonds on the open market. On a day where there are excess reserves in the banking system, the central bank sells bonds and therefore removes reserves from the banking system, as private individuals pay for the bonds. On a day where there are not enough reserves in the system, the central bank buys government bonds from the private sector, and therefore adds reserves to the banking system.
It is important to note that the central bank buys bonds by simply creating money—it is not financed in any way. It is a net injection of reserves into the banking system. If a central bank is to maintain a target interest rate, then it must necessarily buy and sell government bonds on the open market in order to maintain the correct amount of reserves in the system.”
Rather than a modern theory, this is effectively the priests coming out of their guilds to tell the masses how the monetary system works.
They argue for example that the textbook multiplier of savings, as in banks can lend 10 dollar for every dollar in savings, is deceptive.
They argue so very rightly because the Bank of England itself has come out to say that commercial banks, like Goldman Sachs, create money out of nothing when they approve a loan.
In summary, in the current monetary system every entity, except for commercial banks and governments, transacts with money created by commercial banks when they make a loan.
So if you borrow $100 form Goldman Sachs, at that point $100 is created from thin air. This $100 is then destroyed when you pay it back, but where interest goes or where it comes from has not been explained.
When the bank creates this money out of nothing and gives it to you, it demands a further $20 as interest payment on that $100.
Fed has stated that if the public knows how this $20 works, there is “a high risk that it will trigger political controversies.”
We suspect this $20 becomes central bank money (or reserve money as they call it), meaning in effect commercial banks create central bank money from nothing.
While we all transact with each other on Goldman Sachs IoUs, commercial banks transact with each other only with central bank money.
The central bank is the banker of commercial banks and the government. Goldman Sachs likewise borrows from Fed and the moment it does, new money is created that Goldman Sachs can now use to transact with other commercial banks.
Just as we get savings accounts, Goldman Sachs too can park “its” money on Fed and get a savings rate increase of money.
So far, what the MMT theorists are saying is quite obvious. For new money to be created, there has to be demand for new loans. If there is no such demand, money might be destroyed more quickly than created. They argue the government should then step in at this point and create such demand by investing in infrastructure or whatever.
But we are not yet finished with this in a nutshell explanation of the current monetary system at least as far as we understand it because there is another base layer.
While we transact with each other through commercial banks and commercial banks transact with each other through central banks, the central banks transact with each other through the Bank for International Settlements (BIS).
This is the most secretive institution in existence and here central bankers meet in private, ranging from the semi-communist China, semi-authoritarian Russia, Arab monarchies, the free European nations and the Fed, as well as every other nation’s central bank.
In these closed door meetings they coordinate global monetary (and otherwise) policy, including such mundane things as: from now on cryptocurrencies should be called crypto-assets according to a South African central bank official.
While we transact with each other in commercial bank money and commercial banks transact with each other in central bank money, central banks transact with each other in gold.
That is why they stock pile gold and that is why USA was willing to let free some ISIS fighters in return for $2.1 billion worth of physical gold.
That $2.1 billion number misleads. Physical gold is far more scarce, but the point is the current financial system does still have some basis in reality. It is not completely make believe. That is why when banks went under they had to take our wealth, rather than just print new money which they did in addition anyway.
That is why the MMT neo-chartists (charta being a token in latin) or Keynesians or perhaps even Marxists, are open to criticism, but in many ways they are just stating more clearly how the current monetary system works above the BIS level.
It is the case that the central bank can create money out of nothing depending on demand for loans or depending on its willingness to buy government debt from commercial banks. About 6% of the profit from this operation then goes to Goldman Sachs and other commercial banks, with the rest going to the Treasury.
It is also the case that the government itself doesn’t own any money for money is a very abstract concept that begins by the central bank creating it from nothing with its only constrain being whether it needs to pay in gold another central bank.
Thus in the very abstract, the government can create as much money as it likes with the practical constraint being how much it can tax and thus how much of the created money it can destroy through taxation to keep in check inflation, which is just another way of saying the taking of monetary supply out of circulation.
This is very much how the system works and it is one reason why some think the American economy is somewhat communistic for the state through its supply and contraction of money – whether directly or indirectly – can control the entire economy and since the state obviously can’t possibly know the right level of supply or contraction, we get depressions, we get banking collapses, and we get hyperinflation.
Bitcoin, cryptos, and the idea of free market money more generally where everyone is free to issue a currency and to manage it, are an alternative to this command economy because the value of money here is not implemented by the force of taxation, fines, or licensing requirements, but by the free choice of potentially billions of actors around the globe who by the regard of their own interest judge every second whether the service cryptos provide is useful to them or otherwise.
The control of our economy through certain gigantic corporations that do work with the government has been stated for long as a danger of certain communistic ideas that took root last century with Friedrich Hayek pronouncing a few decades ago in the Denationalization of Money that if we do not have free market money, like bitcoin, we will end up in a state economy like USSR.
MMT, therefore, is more of a brazen dive in that direction rather than something the current priests of economics are not currently preaching in any event.
As far as these pages are concerned, not one economist has our ear until they explain how interest is meant to operate in any fiat system, whether current or modern, but judged somewhat impartially, as far as the fiat system is concerned and within its constraints – regardless of whether we agree with the system itself or otherwise – MMT does appear to be at least more transparent.
We can vote out our elected politicians, while Fed’s secret meetings have no accountability.
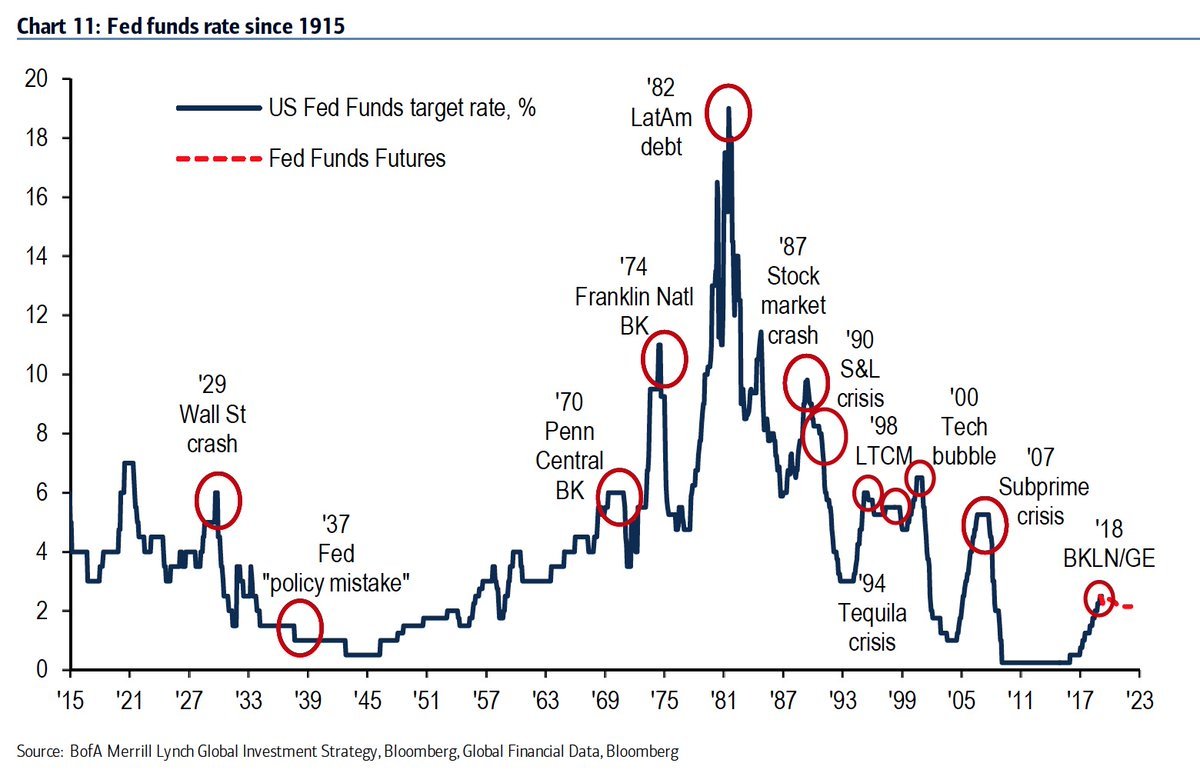
Fed interest rate rises and their crashing of the economy over a century, April 2019.
As much as we think representative democracy has quite a few faults – they did elect Hitler after all – we can at least shout at whoever happens to be the President or Prime Minister and through pressure, including by taking to the streets – thus putting their heads on the line – we can potentially have the option of changing course.
As we have seen recently in the Trump v Fed battle, that still applies to some extent, but if things go wrong a niche would blame Greenspan (or obviously current Fed chair Powell) rather than perhaps the entire civil service.
MTT at least in a way brings some accountability. We’ll know to blame the government and vote them out. While as it stands you have Greenspans running the economy for so many years regardless of whether the politicians change for Fed remains completely unaccountable unless the president himself shouts at them.
So within the very limited constraints of the current financial system, we have no interest in taking any position regarding MTT. But if the view is enlarged to include potential alternatives, it appears somewhat clear that MTT – or whatever other centrally commanded fiat system – will go wrong and as that is the case, then it appears somewhat clear that cryptos are at least an insurance which guarantees freedom for there is no abstraction here beyond: let it be 21 million coins.
Source